what command would you enter to count the number of processes running under your account?
ps (processes status) is a native Unix/Linux utility for viewing information apropos a option of running processes on a system: it reads this information from the virtual files in the /proc filesystem. It is one of the important utilities for system assistants specifically under process monitoring, to aid you understand whats is going on in a Linux organisation.
It has numerous options for manipulating its output, however, you'll find a small number of them practically useful for daily usage.
Read Also: All You Demand To Know About Processes in Linux [Comprehensive Guide]
In this article, nosotros'll look at thirty useful examples of ps commands for monitoring active running processes on a Linux system.
Note that ps produces output with a heading line, which represents the meaning of each cavalcade of information, you lot can notice the significant of all the labels on the ps man page.
List All Processes in Electric current Vanquish
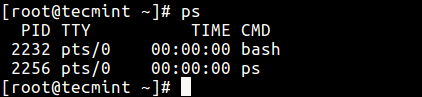
one. If you run the ps command without any arguments, information technology displays processes for the current beat.
$ ps
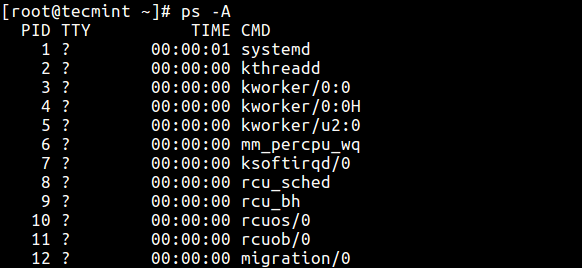
Print All Processes in Unlike Formats
2. Display every active process on a Linux arrangement in generic (Unix/Linux) format.
$ ps -A OR $ ps -eastward
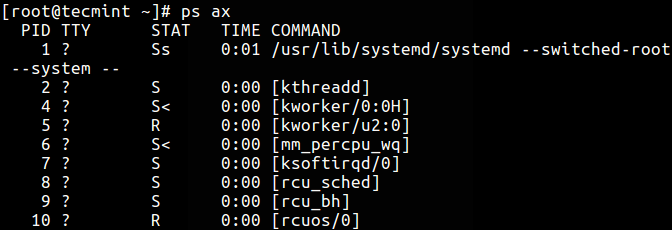
3. Display all processes in BSD format.
$ ps au OR $ ps axu
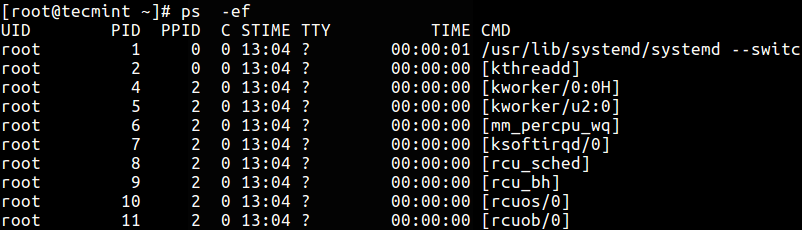
4. To perform a full-format listing, add together the -f or -F flag.
$ ps -ef OR $ ps -eF
Display User Running Processes
5. You lot tin select all processes owned by yous (runner of the ps command, root in this instance), type:
$ ps -x
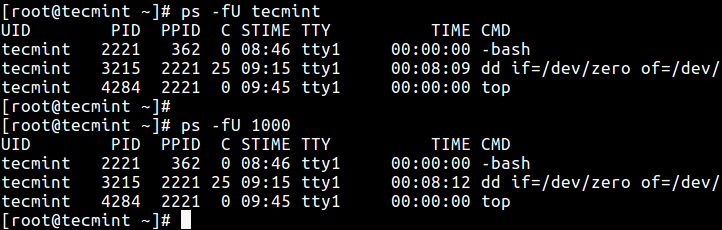
six. To display a user'south processes by real user ID (RUID) or name, apply the -U flag.
$ ps -fU tecmint OR $ ps -fu 1000
vii. To select a user'south processes by constructive user ID (EUID) or name, utilize the -u selection.
$ ps -fu tecmint OR $ ps -fu 1000
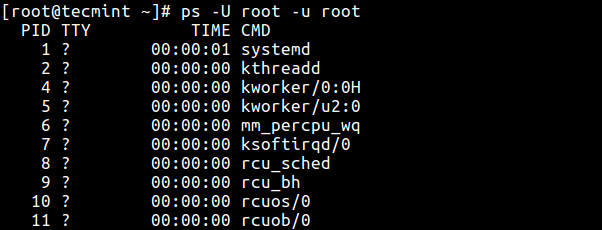
Print All Processes Running as Root (Existent and Effective ID)
8. The command below enables y'all to view every process running with root user privileges (existent & effective ID) in user format.
$ ps -U root -u root
Display Group Processes
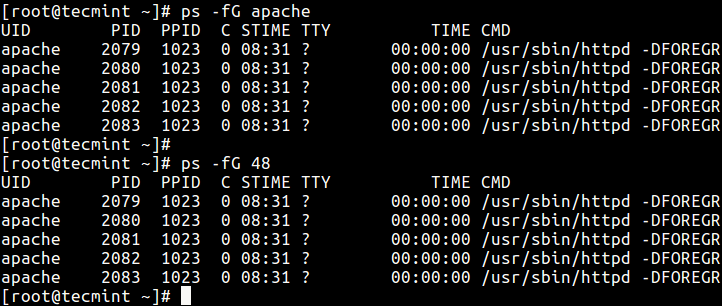
9. If y'all want to listing all processes owned past a certain group (real group ID (RGID) or proper noun), type.
$ ps -fG apache OR $ ps -fG 48
10. To listing all processes owned by effective grouping name (or session), type.
$ ps -fg apache
Display Processes past PID and PPID
eleven. You can list processes by PID as follows.
$ ps -fp 1178

12. To select process by PPID, type.
$ ps -f --ppid 1154
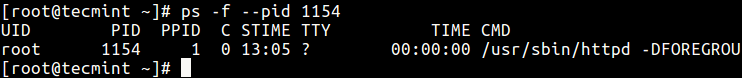
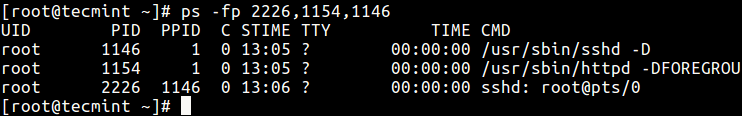
13. Make a choice using a PID list.
$ ps -fp 2226,1154,1146
Display Processes by TTY
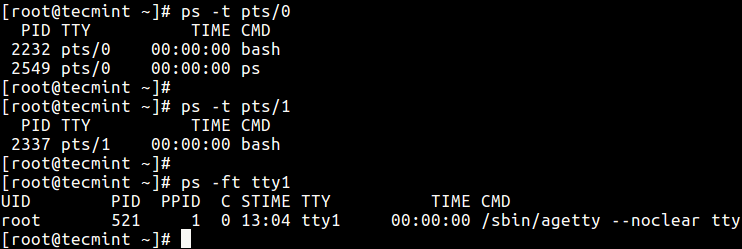
14. To select processes past tty, utilise the -t flag as follows.
$ ps -t pts/0 $ ps -t pts/1 $ ps -ft tty1
Print Process Tree
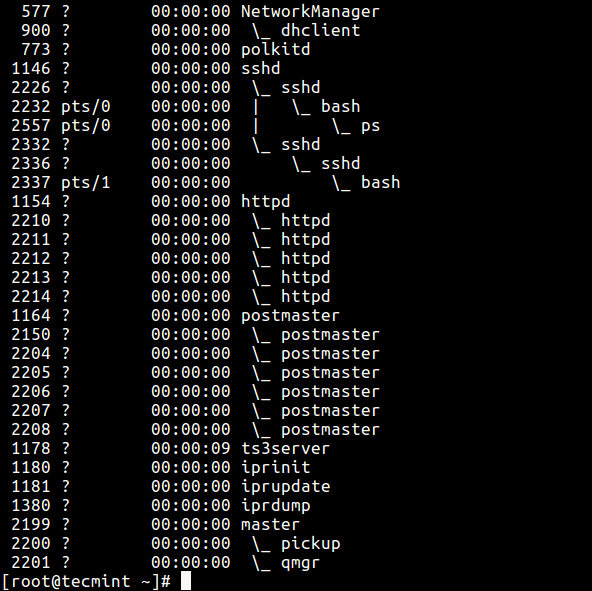
15. A process tree shows how processes on the system are linked to each other; processes whose parents accept been killed are adopted past the init (or systemd).
$ ps -east --forest
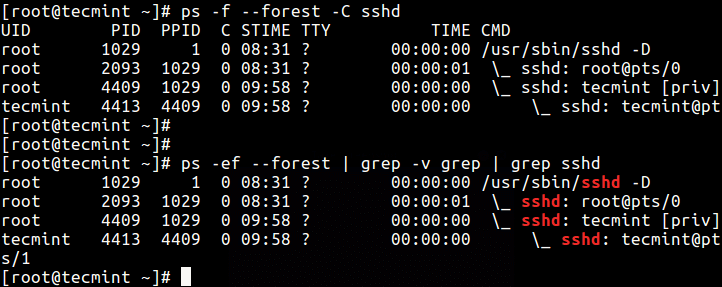
sixteen. You tin also print a procedure tree for a given process similar this.
$ ps -f --forest -C sshd OR $ ps -ef --forest | grep -5 grep | grep sshd
Impress Procedure Threads
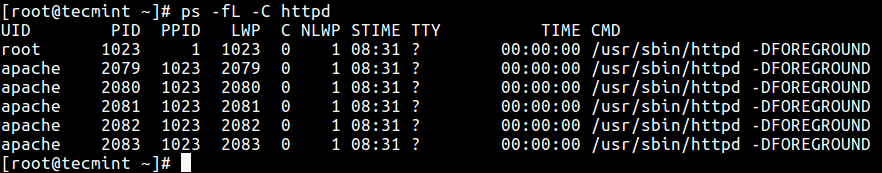
17. To print all threads of a process, use the -L flag, this will prove the LWP (lightweight procedure) as well as NLWP (number of the lightweight processes) columns.
$ ps -fL -C httpd
Specify Custom Output Format
Using the -o or –format options, ps allows yous to build user-defined output formats every bit shown below.
18. To list all format specifiers, include the Fifty flag.
$ ps L
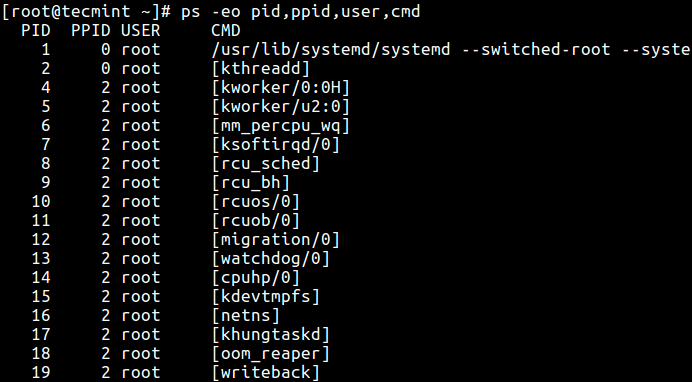
19. The command beneath allows you lot to view the PID, PPID, user name, and control of a process.
$ ps -eo pid,ppid,user,cmd
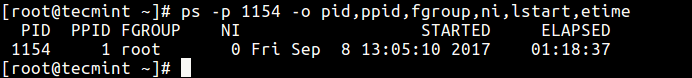
20. Below is another example of a custom output format showing file system grouping, nice value, start time, and elapsed time of a procedure.
$ ps -p 1154 -o pid,ppid,fgroup,ni,lstart,etime
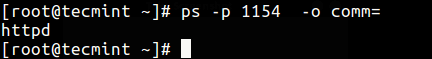
21. To find a process name using its PID.
$ ps -p 1154 -o comm=
Display Parent and Kid Processes
22. To select a specific process by its name, use the -C flag, this will likewise display all its child processes.
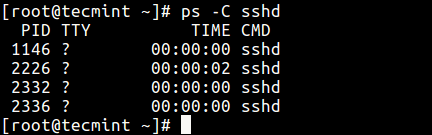
$ ps -C sshd
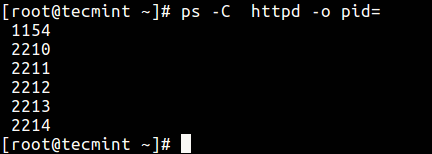
23. Find all PIDs of all instances of a process, useful when writing scripts that demand to read PIDs from an std output or file.
$ ps -C httpd -o pid=
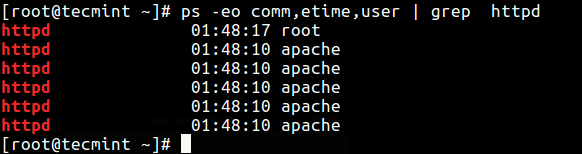
24. Bank check the execution fourth dimension of a process.
$ ps -eo comm,etime,user | grep httpd
The output below shows the HTTPD service has been running for 1 hr, 48 minutes, and 17 seconds.
Troubleshoot Linux System Performance
If your system isn't working as it should be, for instance, if it's unusually slow, y'all can perform some organization troubleshooting equally follows.
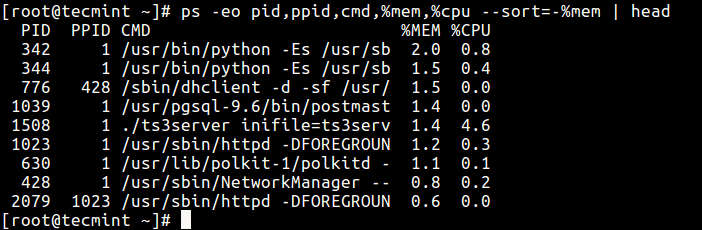
26. Find peak running processes past highest retentivity and CPU usage in Linux.
$ ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu --sort=-%mem | head OR $ ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu --sort=-%cpu | head
27. To impale Linux processes/unresponsive applications or any process that is consuming high CPU time.
First, observe the PID of the unresponsive process or awarding.
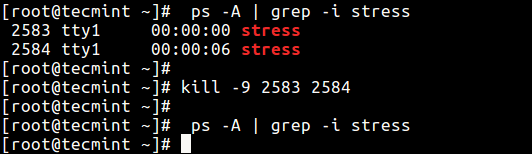
$ ps -A | grep -i stress
Then use the impale control to terminate it immediately.
$ kill -nine 2583 2584
Print Security Data
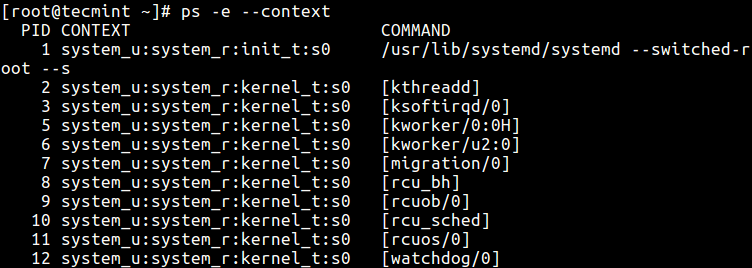
28. Show security context (specifically for SELinux) similar this.
$ ps -eM OR $ ps --context
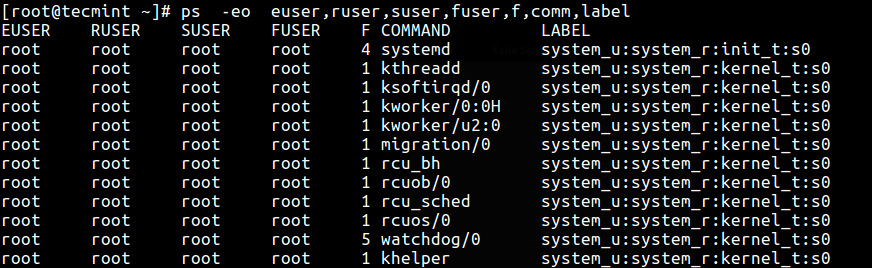
29. You can also display security information in a user-divers format with this command.
$ ps -eo euser,ruser,suser,fuser,f,comm,label
Perform Existent-time Process Monitoring Using Watch Utility
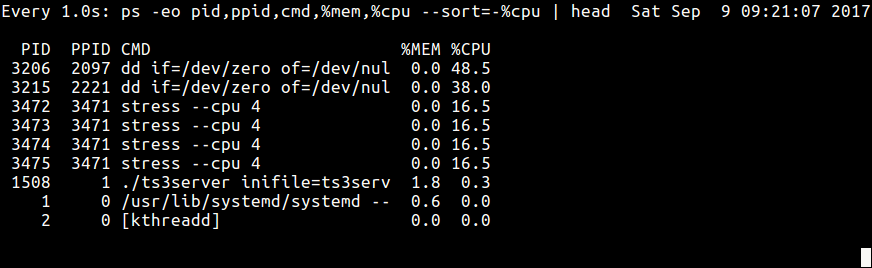
30. Finally, since ps displays static information, you can apply the sentry utility to perform real-time process monitoring with repetitive output, displayed after every 2d as in the control below (specify a custom ps control to achieve your objective).
$ watch -n 1 'ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu --sort=-%mem | caput'
Important: ps but shows static information, to view ofttimes updated output you lot can utilize tools such as htop; tiptop, and glances: the concluding 2 are in fact Linux system performance monitoring tools.
You might also like to read the following related articles.
- How to Find a Process Name Using PID Number in Linux
- Find Top Running Processes past Highest Memory and CPU Usage in Linux
- A Guide to Kill, Pkill, and Killall Commands to Stop a Process in Linux
- How to Find and Kill Running Processes in Linux
- How to Outset Linux Command in Background and Detach Process in Concluding
That's all for now. If you have any useful ps command instance(due south) to share (not forgetting to explain what it does), use the comment form below.
dominquezbosion38.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.tecmint.com/ps-command-examples-for-linux-process-monitoring/
0 Response to "what command would you enter to count the number of processes running under your account?"
Post a Comment